Download our CREAM Certificate here Today, the demand for efficient splicing systems has become increasingly important due to the increased construction complexities, design requirements, escalating costs and limitations of traditional lap splicing methods. This has driven the need for alternatives that is able to provide both structural robustness and cost effectiveness. With all these catastrophes all around the world, Malaysia has been exposed to the stark reality that we can no longer be considered immune to such tragedies of tragic proportions in terms of lives lost, property destruction and even economic collapse. The government and regulatory bodies have therefore taken serious steps in reviewing current building regulations and codes, to enable structural engineers and constructors to take immediate and necessary precautions to ensure the safety of their design as they are liable if anything happened to the buildings (refer provisions under CIDB act below). MOMENT JT mechanical connections conform fully with applicable codes including BS 8110 Pt 1:1997 Clause 3.12.8.16.2 Bar in Tension and ISO 15835, providing defined ductile behaviour and performing like a continuous reinforcing bar. In reinforced concrete design, the Structural Engineer is faced with the task of determining where and how reinforcing bars must be spliced in a structure. This must be done to ensure that the national regulations are adhered to and also to make sure that the structure will not suffer a progressive collapse if overloaded. Due to the minimum connection strength required, it is generally assumed in design that the occurrence of a mechanical connection of two reinforcing bars does not result in a reduction of the anticipated structural strength nor the longitudinal ductility of the reinforcing steel. This would maintain the properties which the reinforced concrete member would have had with a continuous unspliced bar. That is, it is assumed that the use of a mechanical connection does not introduce a structural weakness that could jeopardize the overall structural performance. Design requirements of the applicable codes as in BS 8110 and EN 1992-1 generally assume a minimum connection strength but are silent on the details about test methods and conformity assessment. ISO 15835, which is used as the basis for CREAM’s assessment covers all aspects of coupler production and assessment including: In a structure undergoing inelastic deformations during an earthquake, the tensile stresses in reinforcements may approach the tensile strength of the reinforcements. The requirements for MOMENT JT mechanical splices are intended to avoid a splice failure when the reinforcement is subjected to expected stress levels in the plastic regions. In addition to that, in plastic hinge regions, the first part to fail is the concrete where excessive spalling occurs. Once the concrete spalls, the lap splice behaviour is severely compromised, whereas the mechanical splice behaviour remains intact. In seismic consideration: MOMENT JT connection offers many advantages to the designer and builder to help improve the design and reduce construction time and cost while providing versatility and can help to solve many construction problems today. As Malaysia progresses in nation-building, federal governance, regulations and codes for construction regarding seismic frame construction become more stringent, MOMENT JT connections, the proven mechanical splice method, provides you with the ability to design and build concrete structures to withstand the test of time.Why So Many Construction Structures Collapsed- How Safe Are We?

*MS 2500 (Profile) Enforced 1 December 2016 Consultation with industry and testing body on 5 January 2017: Testing requirements for design requirements are not clearly stated. The meeting agreed to adopt AS4600 and EN9590 Part 5 in addition to MS2500. CIDB has submitted the MS2500 revise application to DSM on January 6, 2017.MOMENT JT Connection
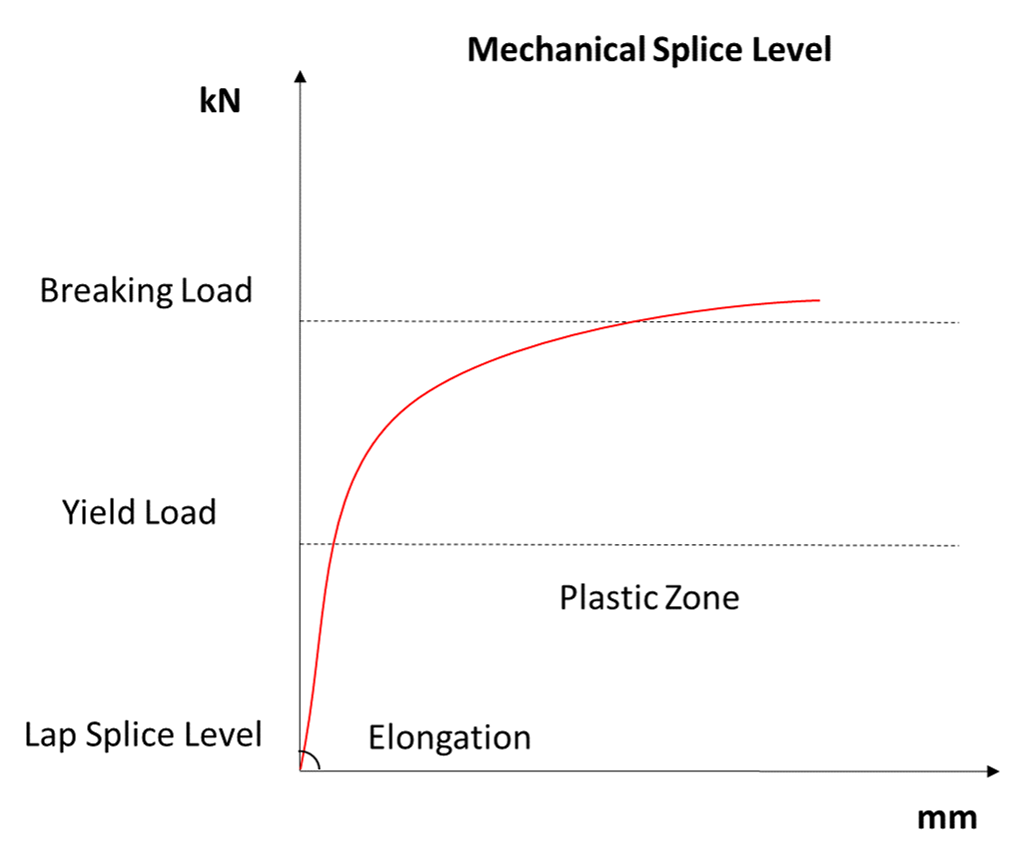
Fig 1: MOMENT JT connections perform beyond the yield point of the bar whereas Lap Splices are only defined in the elastic area. This indicates that the MOMENT JT connection which works as a continuous bar provides additional strength and safety all around independent of the quality of the surrounding concrete.Design Codes and Specifications
MOMENT JT Connection and Seismic Design

Lap Splices (2011 – Turkey) – Concrete spalling results in lower or zero capacity as the concrete that is critical in the load transfer has disappeared.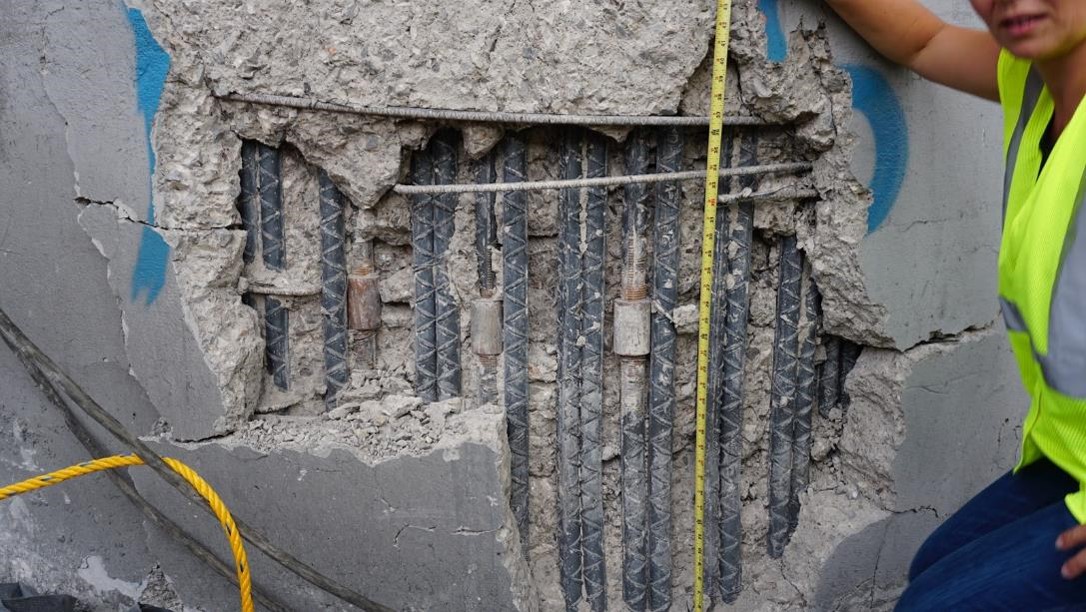
Mechanical Splices (2017 – Mexico City) – Concrete spalling has no effect on capacity as the mechanical connection is still present.
Conclusion

Locally Approved Couplers For Quality Connections.
Let Us Drop You A Call For Consultation. For Free.
Related Products You May Be Interested

[First in Malaysia] CIDB CREAM Certified MOMENT Mechanical Splicing System
Leviat is proud to announce that we are the first company in Malaysia to receive quality certification in accordance to ISO 15835 standard by the Construction Research Institute of Malaysia (CREAM), an independent and transparent certification body in Malaysia under CIDB.